C-RAMAN System
Robotically Assisted MAgnetic Navigation System for Capsule Endoscopy
Background
Background
Digestive system diseases
- Capsule endoscope has been developed for the endoscopic examination of small intestine which cannot be easily reached by wired endoscopic devices. The 1st generation of CE is passively driven by peristalsis of small intestine, and they cannot examine other digestive system such as esophagus, stomach, and large intestine.
- The 2nd generation of capsule endoscope with a permanent magnet inside and driven by external magnetic field, has been developed to actively examine the gastrointestinal tract.
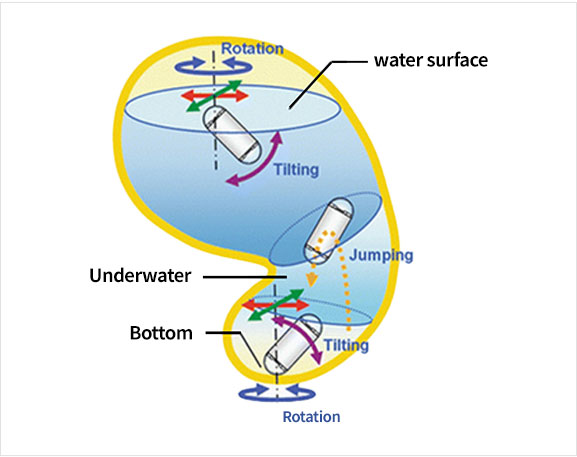
Required motion of capsule endoscope in the stomach

The 1st and 2nd generation of capsule endoscope
Problem
- To control the motion of the magnetically actuated capsule endoscopes, both the manual controllers operated by medical personnel and the robotic controllers using robot arms to control big permanent magnets have been developed and are commercialized.
- For the hand-held magnetic controllers where medical personnel manually manipulate external permanent magnets, it is very difficult to control the precise motion of a capsule endoscope, and the weight of several kilograms results in the fatigue of medical personnel during prolonged examinations.
- For the robot-based magnetic controllers where robot arms manipulate permanent magnets, it is very difficult to generate accurate tilting motion of a capsule endoscope because rotating motion of one permanent magnet cannot generate tiling motion as well as translational motion of a capsule endoscope at the same time.
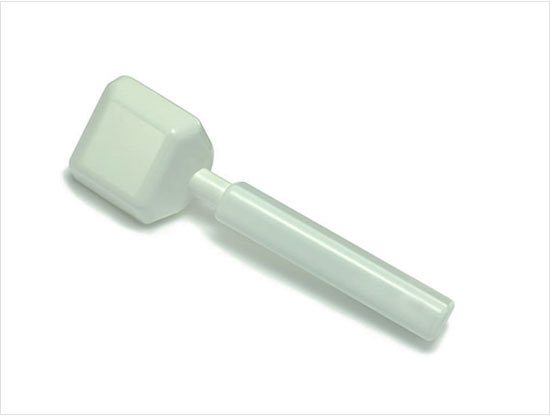

A hand-held type of a magnetic controller
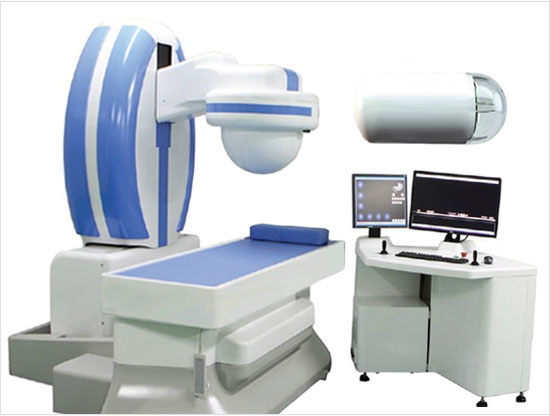
A robot-based magnetic controller
New paradigm

