I-RAMAN System
Robotically Assisted MAgnetic Navigation System for Intervention
Background
Background
Occlusive vascular disease (OVD)
- OVD occurs when a blood vessel becomes narrowed or blocked due to accumulated blood clots or lipids.
- OVD develops into peripheral artery disease, myocardial infarction, and stroke.
- The incidence rate is steadily increasing due to meat-centered dietary habits and an aging society.
- It accounts for 44% of global deaths and is a critical health issue to overcome (Global health issue).

Progress of OVD

Major causes of human death
Problem
Inaccurate procedure
Long hours of operation
Conventional endovascular intervention
OVD is widely treated by an endovascular intervention in which guidewires and catheters are manually inserted into a target lesion and drug delivery, ballooning, and stent installation are performed based on X-ray images.
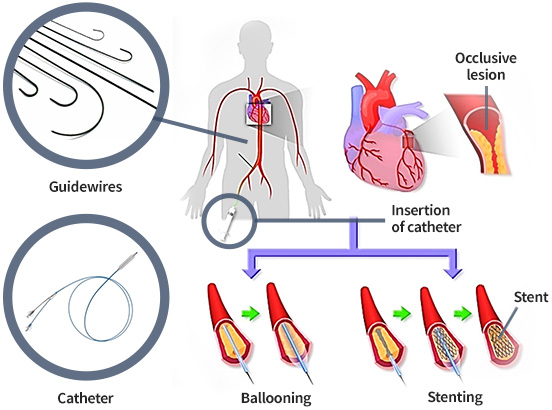
Endovascular intervention to treat OVD

Complicated endovascular intervention
Conventional guidewires and catheters have difficulty in achieving precise force and torque control at their tips.
- Complex procedures including repeated insertion and removal of multiple guidewires and catheters are required.
- Difficulty in precise navigation of blood vessels leads to lengthy procedure times (several hours in cases of total OVD).
- The accuracy and success rate of the procedure are highly affected by the practitioners’ hand techniques or proficiency.
- Many lesions are unreachable with conventional equipment, such as the M3 and M4 segments of the middle cerebral artery.
- Guidewires and catheters may cause perforation or bleeding (24.7% of patients experience cerebral bleeding in cerebral arteries).
- It is impossible to remove stents afterward once installed into the blood vessels.
- In cases of total OVD, intravascular path is not visible.
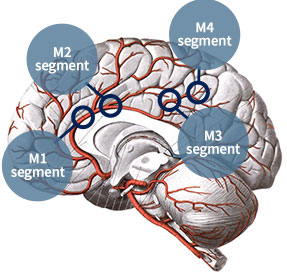
Segments of the middle cerebral artery
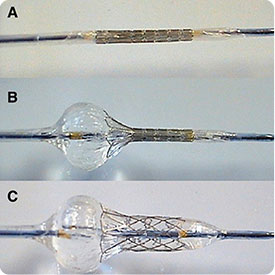
Incorrect stent installation

Total OVD requiring several hours of operation
Severe radiation exposure
Medical staff are continuously exposed to severe radiation from X-ray machines during procedures.
- To verify the position of lesions, guidewires, and catheters, medical staff perform procedures close to X-ray machines.
- X-ray radiation is fatal to health, increasing the incidence of cancer and cataracts.
- To minimize radiation exposure, medical staff wear heavy lead protective gear during long procedures.
- The weight of the protective gear can accumulate stress on the neck and spine, potentially causing surgical disabilities.
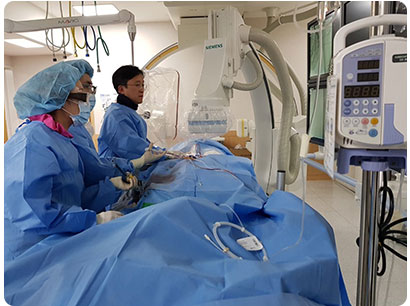
Medical personnel wearing radiation protective clothing to perform endovascular interventional procedure near an X-ray imaging device

Increase in cancer risk due to radiation exposure (10% increase in cancer risk with 1,000 mSv over 20 years for medical practitioners)
A new paradigm for endovascular intervention is required.


Examples of applicable occlusive vascular and non-vascular diseases.

